EXAM
Questions:
Please go through the patient data in the links below and answer the following questions:
1) A 55 year old man with Recurrent Focal Seizures
Detailed patient case report here: http://ushaindurthi.
blogspot.com/2020/11/55-year- old-male-with-complaints-of. html 1. What is the problem representation of this patient and what could be the anatomical site of lesion ?
A 55 year old male, construction worker with Type2 DM, who is a chronic alcoholic & smoker, came with c/o weakness of right upper limb with involuntary movements of both right UL & LL
2. Why are subcortical internal capsular infarcts more common that cortical infarcts?
Subcortical areas are supplied by penetrating branches that arise from initial segments of the arteries near the Circle of Willis at the base of the brain.Occlusion of these penetrating arteries result in subcortical infarcts. These penetrating arteries arise at acute angles from major vessels and are thus, anatomically prone to constriction and occlusion. So subcortical infarcts are more common than cortical infarct.
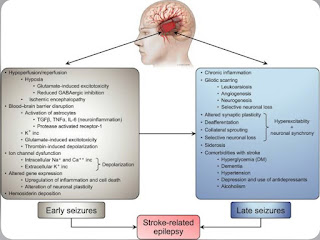
3. What is the pathogenesis involved in cerebral infarct related seizures?
4. What is your take on the ecg? And do you agree with the treating team on starting the patient on Enoxaparin?
ST depressions noted in precordial leads V1 to V6
Yes,I agree with the team on starting Enoxaparin
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012369216329579
5. Which AED would you prefer?
Carbamazepine
If so why?
It binds preferentially to voltage-gated sodium channels in their inactive conformation, which prevents repetitive and sustained firing of an action potential.
Please provide studies on efficacies of each of the treatment given to this patient.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29243813/
Question 2) 55 year old man with Recurrent hypoglycemia
Questions:
1. What is the problem representation for this patient?
A 55 year old male with Type2 DM came with c/o exertional dyspnea and cough since 3 days, patient complained of sudden onset of giddiness and profuse sweating secondary to OHA induced hypoglycemia
2. What is the cause for his recurrent hypoglycemia? And how would you evaluate?
Drug induced hypoglycemia
Features of renal failure—> decreased excretion of OHAs—-> increased duration of action—> lead to hypoglycemia
3. What is the cause for his Dyspnea? What is the reason for his albumin loss?
Obesity might be the cause of dyspnoea because it increases the work load of breathing
albuminuria<—Diabetic nephropathy
CUE/ urine cultures are not available,which would compliment the use of antibiotics.
3(A)
Case details here: https://
1. How would you evaluate further this patient with Polyarthralgia?
2. What is the pathogenesis involved in RA?
Efficacy and safety of various anti-rheumatic treatments for patients with rheumatoid arthritis:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6348345/
3(B)75 year old woman with post operative hepatitis following blood transfusion
Case details here: https://
1.What are your differentials for this patient and how would you evaluate?
-Post transfusion hepatitis
- Lasix & Nebulization —for wheeze and crepts
- Lactulose —To prevent hepatic encephalopathy
- Zofer — For vomitings
- Pantop —To prevent gastritis
http://manojkumar1008.
1. What is the problem representation of this patient?
A 60 year old female with Type2 DM presented with c/o pricking type of chest pain since 4 days and uncontrolled sugars with GRBS being 585
2. What are the factors contributing to her uncontrolled blood sugars?
Consolidation noted in the right upper lobe
4. What do you think is the cause for her hypoalbuminaemia? How would you approach it?
- Inflammation
- Malnutrition
- Albuminuria
- Piptaz & clarithromycin : for sepsis
- Egg white & protien powder : for hypoalbuminemia
- Lactulose : for constipation
- Actrapid / Mixtard : for hyperglycemia
- Tramadol : for pain
- Pantop : to prevent gastritis
- Zofer : to prevent vomitings
Case report here: https://appalaaishwaryareddy.
1. What is the anatomical and pathological localization of the problem?
2. How do you approach and evaluate this patient with Hepatitis B?
3. What is the pathogenesis of the illness due to Hepatitis B?
Yes , separate machines must be used for patients known to be infected with HBV (or at high risk of new HBV infection)
5. What are the efficacies of each treatment given to this patient? Describe the efficacies with supportive RCT evidence.
- Lactulose : for prevention and treatment of hepatic encephalopathy. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27089005/
- Tenofovir : for HBV
- Octreotide : for upper GI bleed. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11999818/
- Lasix : for fluid overload (AKI on CKD)
- Vitamin -k
- Pantop : for gastritis
- Zofer : to prevent vomitings
- Monocef (ceftriaxone) : for AKI (? renal)
6) 58 year old man with Dementia
Case report details: http://
1. What is the problem representation of this patient?
A 58 year old weaver, occasional alcoholic came with c/o slurring of speech , deviation of mouth to right side associated with drooling of saliva , food particles and water predominantly from left angle of mouth and smacking of lips since 6 months.
2. How would you evaluate further this patient with Dementia?
Yes
5. Are you aware of pharmacological and non pharmacological interventions to treat such a patient and what are their known efficacies based on RCT evidence?
- Donepezil
- Rivastigmine
- Galantamine
- Memantine
7) 22 year old man with seizures
Case report here http://geethagugloth.
1. What is the problem representation of this patient ? What is the anatomic and pathologic localization in view of the clinical and radiological findings?
2. What the your differentials to his ring enhancing lesions?
3. What is "immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome IRIS and how was this patient's treatment modified to avoid the possibility of his developing it?
As his CD4 count is > 50 /mm3 consider delayed initiation of ART ideally after 8 weeks of starting ATT to reduce the chances of developing IRIS











Comments
Post a Comment